Next: Two-dimensional Simulations Up: Detonations with Detailed Hydrogen-Oxygen Previous: Detonations with Detailed Hydrogen-Oxygen
Initial conditions
Analogous to the one-step detonation model, the Euler equations for thermally perfect gas-mixtures with detailed chemical reaction can be solved exactly, if we assume a planar stationary detonation wave propagating with constant speed. For the following simulations we use the planar one-dimensional solution for a H2:O2:Ar Chapman-Jouguet detonation with molar ratios 2:1:7 at T0=298 K and p0=6.67 kPa or p0=10.0 kPa as initial condition. For p0=6.67 kPa the detonation is shown in Fig. 3.1. The induction length lig for this configuration is approximately 1.4 mm.
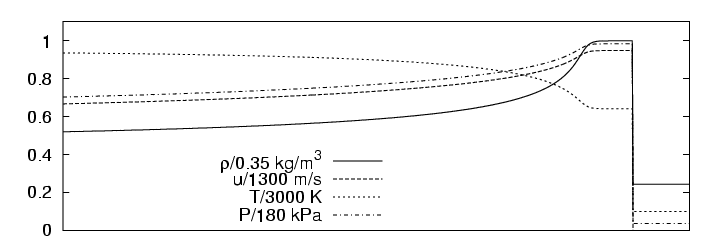
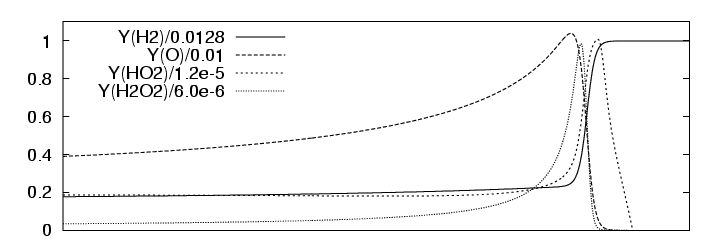
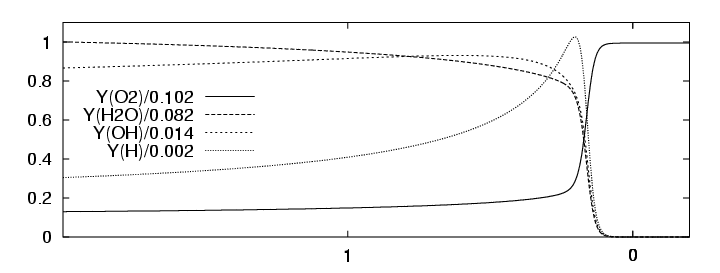
|
Next: Two-dimensional Simulations Up: Detonations with Detailed Hydrogen-Oxygen Previous: Detonations with Detailed Hydrogen-Oxygen
Table of Contents Home Contact