Next: Reaction Terms of Detailed Up: Numerical Simulations of Gaseous Previous: Numerical Simulations of Gaseous
Multi-component Euler Equations
The governing equations of gaseous detonations are the multi-component Euler equations with chemical reactive source terms. These equations can be written in conservation form with K inhomogeneous continuity equations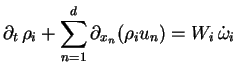 for
for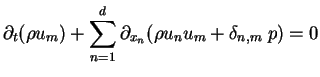 for
for![$\displaystyle \displaystyle \partial_t (\rho E) +\sum_{n=1}^d
\partial_{x_n} \left[u_n (\rho E+p)\right] = 0 \;. $](img5.gif)
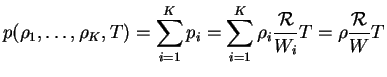
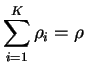 and
and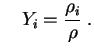
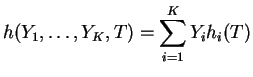 with
with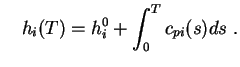
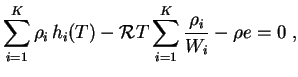
Subsections
Table of Contents Home Contact